- 10-15 Min Read
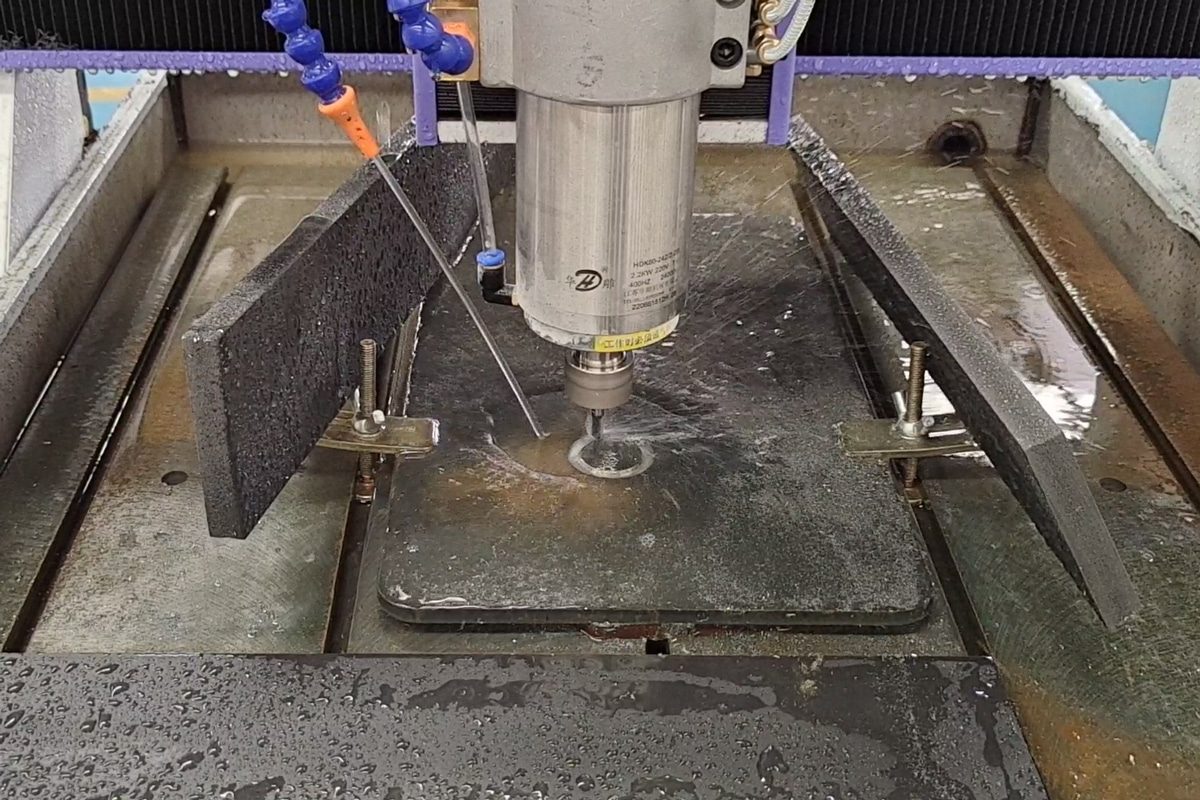
Metal CNC routers generate significant heat during operation due to high-speed spindle rotation, prolonged cutting cycles, and constant friction between the tool and workpiece. Without effective cooling, this heat can lead to premature tool wear, reduced dimensional accuracy, and even damage to critical machine components. To address these challenges, metal CNC routers rely on a range of cooling methods, each suited to specific parts of the systems.
From simple air-cooling systems to more advanced water or mist-based solutions, understanding the right cooling approach is key to ensuring reliable operation and high-quality output. In this article, we’ll explore the various cooling methods used in metal CNC routers, explain how each method works, and provide practical insights into selecting the right cooling system for your specific machining environment.
Why Cooling is Important for Metal CNC Routing
During high-speed metal cutting, a significant amount of heat is generated at the interface between the cutting tool and the workpiece. As spindle speeds and feed rates increase to boost productivity, the intensity of this heat also rises. Why is cooling important for metal CNC routing?
Effects of Excessive Heat
Overheating during metal CNC routing can significantly compromise machining performance and product quality. Its effects are most evident in three key areas:
- Tool Wear and Breakage: Excessive heat accelerates the wear of cutting tools, especially at the cutting edge where friction is most intense. Prolonged exposure can lead to edge chipping, deformation, or complete tool breakage.
- Thermal Expansion and Precision Loss: Overheating causes both the workpiece and critical parts of the CNC router to undergo thermal expansion. This expansion shifts dimensions and misaligns tool paths, resulting in reduced accuracy and tolerance errors.
- Material Surface Damage: High heat at the cutting zone may cause discoloration, oxidation, or even micro-cracks in heat-sensitive alloys. In extreme cases, localized melting or the formation of burrs can occur, requiring additional post-processing or rendering the part defective.
Benefits of Proper Cooling
Implementing effective cooling methods in metal CNC routing delivers multiple performance, quality, and maintenance advantages. Here are the key benefits:
- Extended Tool Life: Proper cooling reduces the heat and friction at the cutting edge, which slows down tool wear and helps maintain the integrity of cutting tools over longer production runs.
- Improved Machining Accuracy: By keeping both the workpiece and machine components at stable temperatures, cooling minimizes thermal expansion.
- Enhanced Surface Finish: Cooling prevents material overheating, oxidation, and melting at the cutting zone. This results in smoother surfaces, fewer burrs, and improved edge quality.
- Protection of Machine Components: Cooling systems also help safeguard vital machine parts from heat-related stress and degradation, extending the overall life of the CNC router.
- Stable and Reliable Operation: Proper cooling contributes to consistent cutting performance and process stability, which reduces production variability and supports repeatable, high-quality output.
In metal CNC routing, managing heat is not just a maintenance task—it’s a fundamental requirement for achieving precision, protecting equipment, and maintaining consistent productivity.
Types of Cooling Methods for Metal CNC Routers
Cooling systems for metal CNC routers are key for managing the heat generated during high-speed machining. Different parts of the machine may require specific cooling strategies. Below are the most commonly used types of cooling methods, categorized by their target application and functionality:
Spindle Cooling Methods
The spindle is one of the most heat-sensitive and high-performance components in a metal CNC router. During extended cutting operations, spindles can generate substantial heat. Here are the common spindle cooling methods:
- Air Cooling: Air-cooled spindles use internal or external fans to blow ambient air over the spindle housing, helping to dissipate heat generated during operation. This method is straightforward, affordable, and requires minimal maintenance since it doesn’t involve coolant fluids or additional hardware. However, its cooling capacity is limited, making it less effective for high-speed or continuous metal cutting where excessive heat buildup can reduce spindle lifespan and machining accuracy.
- Water Cooling: Water-cooled spindles circulate chilled water through internal channels around the motor and bearings, absorbing heat and transferring it to an external chiller or radiator system. This method provides superior thermal control and consistent cooling, even under heavy-duty and high-RPM operations. Water-cooled systems are quieter and more effective than air-cooled alternatives, but they require a more complex setup, including pumps, tubing, and regular coolant maintenance to prevent leaks or clogging.
Tool and Workpiece Cooling Methods (Cutting Zone)
During metal CNC routing, the cutting zone experiences intense friction and heat buildup due to continuous contact between the tool and the metal workpiece. Below are the primary cooling methods used at the cutting zone:
- Mist Cooling (MQL – Minimum Quantity Lubrication): Mist cooling combines compressed air with a small amount of lubricant or coolant to form a fine aerosol spray directed precisely at the cutting area. This method significantly reduces heat and friction while using minimal fluid, making it an environmentally friendly and cost-effective option. It is especially effective for light to moderate metal machining tasks, where full flood cooling isn’t necessary. However, mist cooling may not provide sufficient heat removal for high-speed or heavy-duty operations involving harder metals.
- Flood Cooling: Flood cooling delivers a continuous, high-volume stream of coolant directly to the cutting zone, thoroughly soaking both the tool and workpiece. This method is highly effective at removing heat and flushing away metal chips, which reduces tool wear and improves surface finish quality. It is widely used in industrial metalworking environments, particularly for harder materials and demanding operations. However, flood cooling requires a more complex setup, including coolant tanks, pumps, filtration systems, and splash management, along with regular coolant maintenance.
- Compressed Air Cooling: Compressed air cooling uses high-pressure air directed at the tool and cutting area to blow away chips and lower surface temperatures. It is a dry, clean method with no coolant residue, making it ideal for applications where liquid use is impractical or undesirable. Although it helps prevent chip accumulation and provides moderate cooling, it is not sufficient for high-heat applications or hard metal machining.
- Cryogenic Cooling: Cryogenic cooling involves the use of liquid nitrogen (LN₂) or carbon dioxide (CO₂) to cool the cutting area. This method drastically lowers temperatures, enabling precise machining of heat-sensitive or superhard materials. While cryogenic cooling offers exceptional results in advanced or high-performance machining, it comes with higher costs, complex setup requirements, and the need for specialized handling and safety precautions.
Electronics and Control System Cooling
In a metal CNC router, the electronics and control systems are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Effective cooling of the electrical cabinet and control units is beneficial for system stability and safety.
- Fan and Ventilation Cooling: This is the most common and cost-effective method for cooling electronic enclosures. It involves using internal or external fans to circulate ambient air through the control cabinet, expelling hot air and drawing in cooler air. Proper ventilation ensures moderate temperature regulation and is typically sufficient for CNC routers operating in clean, climate-controlled environments. However, its effectiveness is limited in dusty, humid, or high-temperature conditions.
- Air Conditioners and Heat Exchangers: Used in harsh or high-temperature environments to protect sensitive electronics. Air conditioning units or closed-loop heat exchangers are installed on control cabinets to maintain a stable internal temperature, independent of external conditions. These systems prevent dust, humidity, and heat from affecting the electronics, providing consistent thermal protection. While they require higher initial investment and regular maintenance, they are beneficial for high-precision operations.
Integrated Cooling Systems
Integrated cooling systems refer to pre-designed, built-in cooling solutions that are incorporated into the CNC router by the manufacturer. These systems are engineered to work seamlessly with the machine’s components, ensuring optimized thermal management without requiring extensive aftermarket modifications.
Modern metal CNC routers often come equipped with integrated water-cooled spindles, mist lubrication units, and electronic cabinet ventilation or air conditioning, all controlled through the machine’s interface or control software. These systems are typically part of a closed-loop design, which continuously monitors temperature levels and adjusts cooling operations automatically to maintain stable working conditions.
The key advantages of integrated systems include ease of use, compact layout, and efficient coordination between machine functions and cooling performance. They reduce setup complexity, streamline maintenance, and eliminate compatibility concerns between third-party components. It is a valuable feature for manufacturers seeking reliability and simplicity in thermal control.
Selecting the Right Cooling Method
Choosing the appropriate cooling method for a metal CNC router depends on several key factors, each influencing the effectiveness, cost, and maintenance requirements of the system. The right cooling setup not only ensures optimal machine performance but also minimizes tool wear, energy consumption, and downtime.
- Material Type and Machining Intensity: Hard metals like stainless steel or titanium generate more heat during cutting and require more aggressive cooling, such as water or flood cooling. Softer metals like aluminum may perform well with mist or air cooling. For materials sensitive to heat or requiring ultra-precision, cryogenic cooling may be considered.
- Type of Cutting: If you’re performing light-duty operations, such as engraving or machining aluminum or brass with short cycle times, air cooling or compressed air cooling is usually sufficient. For regular metal cutting tasks involving moderate speeds and loads, mist cooling (MQL) provides a good balance. Operations involving stainless steel, carbon steel, or titanium at high spindle speeds or for extended durations demand flood cooling or water-cooled spindle systems.
- Spindle Power and Duty Cycle: Higher spindle power and continuous operation produce more heat, necessitating more efficient cooling systems. Air-cooled spindles may suffice for light-duty work, but high-RPM, industrial applications typically demand water spindles to maintain thermal stability.
- Production Volume and Operating Hours: Shops with high output and long operating hours benefit from robust, automated cooling systems that can maintain consistent temperatures over time. Integrated flood cooling or closed-loop water chillers are ideal for such environments, while low-volume operations may only require basic fan cooling or mist systems.
- Workshop Environment: Ambient temperature, dust levels, and humidity influence the choice of cooling for electronics and enclosures. In clean, temperature-controlled rooms, fan cooling may be sufficient. In hot or dusty environments, sealed control cabinets with air conditioners or heat exchangers are necessary to protect sensitive components.
- Maintenance Capabilities and Resources: Complex cooling systems like water cooling require more maintenance, including coolant level monitoring, periodic cleaning of tanks and filters, and occasional pump maintenance. Businesses with limited technical staff may prefer simpler air-cooled or mist systems for ease of maintenance.
- Budget Constraints: Cost also plays a critical role. Air cooling and compressed air systems are more affordable upfront, but may lack the performance needed for demanding jobs. Advanced cooling options like oil or cryogenic systems offer better performance but come with higher costs and installation requirements.
By evaluating these factors in combination, users can determine which cooling methods align best with their specific machining needs, operational goals, and budget. For optimal results, it’s often beneficial to consult the CNC machine manufacturer for tailored recommendations based on the CNC router’s configuration and application.
Best Practices for CNC Cooling System Maintenance
Neglecting CNC cooling system upkeep can lead to overheating, tool failure, and costly downtime. To prevent these issues and keep your machine running at peak performance, it’s necessary to follow a set of proactive maintenance practices. The following best practices will help ensure that your CNC cooling system remains clean, efficient, and fully functional over time.
- Regular Coolant Inspection and Replacement: Check coolant levels daily and top off as needed to prevent pump cavitation and overheating. Replace the coolant according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule or when it becomes dirty, discolored, or contaminated. Fresh coolant improves thermal conductivity and protects against corrosion and bacterial growth.
- Clean and Flush the System Periodically: Over time, coolant lines, reservoirs, and heat exchangers can accumulate sludge, algae, or metal particles. Schedule regular flushing and cleaning of the entire system, including tanks, hoses, and pumps, to prevent clogging and ensure efficient coolant flow.
- Inspect and Maintain Filters and Strainers: Coolant filtration systems should be checked weekly. Clean or replace filters to prevent debris from recirculating, which can cause blockages or damage to sensitive components like pumps or spindle cooling channels.
- Check for Leaks and Hose Integrity: Inspect all coolant lines, connectors, and seals for leaks, cracks, or signs of wear. Even small leaks can lead to reduced cooling performance or electrical hazards if liquid enters sensitive areas. Replace damaged hoses immediately to avoid costly repairs.
- Monitor Pump and Chiller Performance: Ensure that coolant pumps and chillers are operating within their rated parameters. Listen for unusual noises and monitor output pressure and temperature. Any decrease in performance may indicate a buildup, wear, or mechanical issues that require servicing.
- Maintain Proper Airflow in Air-Cooled Systems: For air-cooled spindles and cabinets, clean fan blades, intake grilles, and ventilation filters regularly to prevent dust buildup. Ensure that airflow is unobstructed and that all fans are functioning correctly.
- Log Maintenance Activities: Keep a maintenance log to track service intervals, coolant changes, and component inspections. This helps identify recurring issues and ensures that no critical tasks are overlooked.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Always refer to your CNC machine and cooling system manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance intervals, recommended coolant types, and service procedures. Using the correct products and methods prevents compatibility issues and voided warranties.
Effective cooling system maintenance isn’t just about extending equipment life—it’s about maintaining consistent machining quality, minimizing unplanned downtime, and protecting your investment. Following these best practices will help you get the most out of your cooling system and maintain the overall health of your CNC operation.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with regular maintenance, CNC cooling systems can occasionally encounter issues that disrupt machine performance. Recognizing the symptoms early and applying the correct troubleshooting steps can prevent costly damage and downtime. Below are some of the most common cooling system problems and practical tips for resolving them:
Overheating: Symptoms and Causes
Overheating typically presents as high spindle or workpiece temperatures, rapid tool wear, inconsistent cut quality, or system alarms. It can result from low coolant levels, clogged filters, restricted coolant lines, failing pumps or fans, or poor ventilation. Here are the troubleshooting steps:
- Check coolant levels and refill if necessary.
- Clean or replace clogged filters and flush hoses.
- Verify the operation of pumps and fans; replace if faulty.
- Ensure cabinet ventilation is unobstructed and clean air filters are regularly replaced.
- Use temperature sensors to monitor actual system performance and diagnose abnormalities.
Coolant Not Reaching the Cutting Area
When coolant fails to reach the cutting zone, symptoms include dry cutting noise, smoke, tool overheating, and poor surface finish. This is usually due to disconnected hoses, clogs, misaligned nozzles, or a failing pump. Here are the troubleshooting steps:
- Inspect hoses for damage or disconnection and reconnect or replace as needed.
- Clear blockages in hoses and nozzles using cleaning fluid or compressed air.
- Check that the coolant pump is operational and producing enough pressure.
- Align coolant nozzles to target the tool and work area correctly.
- Review CNC control settings to ensure that coolant delivery is properly activated.
Mist Nozzle Clogging
Clogged mist nozzles result in weak or uneven spray and overheating at the cutting area. This often stems from dried coolant residue, debris, or poor-quality coolant. Here are the troubleshooting steps:
- Remove and inspect the nozzle for visible buildup.
- Soak the nozzle in a solvent and clear it with compressed air or a small brush.
- Flush or replace the coolant supply line if contaminated.
- Use filtered, high-quality coolant to avoid future blockages.
- Install inline filters and schedule regular cleaning of the mist system.
Spindle Running Hot Despite Cooling
If the spindle remains hot even with an active cooling system, possible causes include restricted flow, air pockets in the coolant loop, internal blockages, or sensor malfunctions. Here are the troubleshooting steps:
- Check for consistent coolant flow and address any flow issues.
- Bleed air from the system to eliminate airlocks.
- Inspect coolant condition and temperature; flush or replace if needed.
- Clean internal cooling channels or consult the manufacturer for service.
- Verify the accuracy of temperature sensors and control signals.
- Upgrade the cooling system if it’s underpowered for the spindle’s workload.
CNC cooling system problems often start small but can lead to serious machine damage and production delays if ignored. By paying attention to common symptoms and performing timely troubleshooting, you can maintain smooth, reliable machine operation. If problems persist, it’s always advisable to consult the equipment manufacturer or a qualified technician.
Summarize
Proper cooling is beneficial for the efficient and reliable operation of metal CNC routers. Whether through air, water, mist, or more advanced methods, each cooling approach plays a key role in managing heat, protecting components, and ensuring machining accuracy. The right choice depends on the cutting intensity, machine configuration, and available maintenance resources. By selecting suitable cooling methods and maintaining them regularly, operators can extend tool life, improve performance, and prevent costly downtime.
If you’re looking for a reliable and professional CNC router supplier, AccTek CNC is an excellent choice. As a leading CNC router manufacturer in China, AccTek specializes in producing high-performance machines tailored for cutting, engraving, and milling a wide range of materials, including wood, metal, plastic, stone, and composites. Our commitment to quality, customization, and responsive technical support makes us a trusted partner for businesses seeking efficient and cost-effective CNC machining equipment.
