- 12-17 Min Read
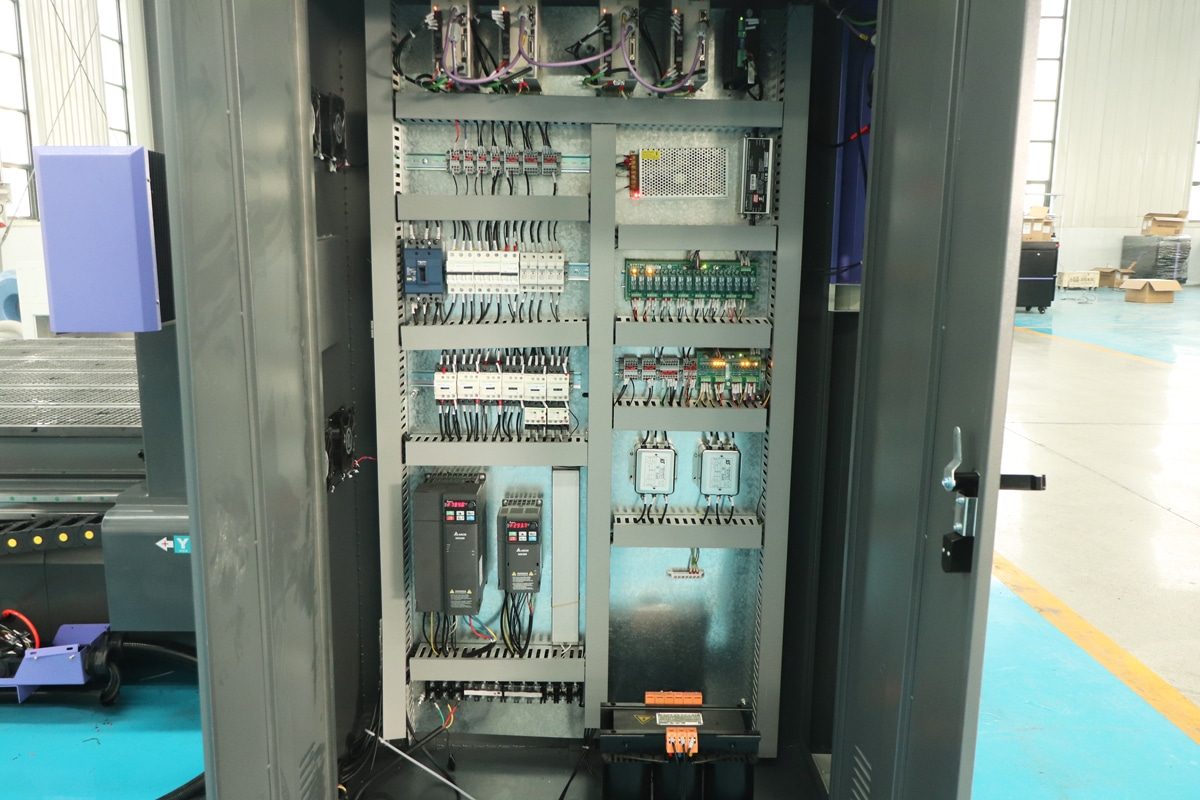
CNC routers have become essential tools in modern manufacturing, offering high precision and automation for cutting, engraving, and shaping materials. However, like all electrically powered machinery, they come with potential safety risks, especially when it comes to electrical systems. Improper wiring, neglected maintenance, or operator error can lead to short circuits, equipment damage, or even serious injury.
Ensuring electrical safety isn’t just about protecting the machine, it’s about safeguarding the workplace and everyone in it. In this article, we’ll explore the key steps to ensure the electrical safety of CNC routers, from proper installation and routine inspections to safe operating procedures and operator training, to provide you with actionable guidance to ensure electrical safety.
Understanding Electrical Risks in CNC Routers
CNC routers rely heavily on electrical power to drive motors, control systems, and other critical components. This makes them vulnerable to various electrical hazards if not properly managed. Understanding these risks is the first step toward ensuring a safe operating environment.
Common Electrical Hazards
- Short Circuits: Short circuits occur when an unintended connection forms between two conductive elements, allowing excessive current to flow. This often results from faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or improperly connected components. Short circuits can cause overheating, sparks, and even electrical fires, making them one of the most dangerous hazards in CNC routers.
- Ground Faults: A ground fault happens when electrical current unintentionally flows to the ground due to insulation failure or exposed wires. This can lead to electrical shock hazards for operators, pose fire risks, and damage machine components. Ground faults are particularly dangerous in high-voltage CNC systems.
- Overloading Circuits: CNC routers draw significant power, especially during high-speed operations. If multiple machines or accessories are connected to an insufficient power supply, the circuit can overload, leading to tripped breakers, overheating, or permanent damage to electrical components.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): The high-frequency signals produced by CNC motors and drives can interfere with other electronic devices and even disrupt the machine’s control system. Without proper shielding, EMI can cause erratic behavior, misalignment, or malfunctions.
- Poor Wiring and Loose Connections: Loose terminal connections, damaged cables, or poor-quality wiring can lead to intermittent electrical failures, overheating, or increased resistance, affecting the overall performance of the CNC router.
- Lack of Safety Features: Without protective electrical components such as fuses, circuit breakers, and emergency stop switches, CNC routers become vulnerable to electrical failures that can escalate into severe hazards.
Potential Consequences of Ignoring Electrical Safety
Failing to address electrical safety risks in CNC routers can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Equipment Damage: Electrical faults can burn out motors, damage control boards, and degrade wiring, leading to costly repairs or complete machine failure. Downtime due to electrical malfunctions can significantly impact production schedules.
- Fire Hazards: Short circuits, overloaded circuits, and exposed wiring can trigger electrical fires, endangering personnel, equipment, and facilities. Fires resulting from CNC routers are often difficult to control due to the involvement of high-voltage components.
- Operator Injury or Fatality: Electrical shocks, arc flashes, or contact with live wires can result in severe injuries or even fatalities. Operators working near unprotected electrical components are at high risk if safety precautions are not followed.
- Production Downtime and Financial Losses: Unexpected machine failures due to electrical issues can lead to costly production stoppages. Frequent downtime can reduce efficiency, delay orders, and increase maintenance expenses.
Understanding these electrical hazards and their consequences highlights the importance of proactive safety measures. The following sections will guide you through the best practices to minimize these hazards and maintain a safe CNC operating environment.
Design and Installation Best Practices
Proper design and installation of a CNC router’s electrical system are beneficial for ensuring safe operation, minimizing hazards, and extending the machine’s lifespan. Following best practices during the setup phase can prevent common electrical issues such as short circuits, power fluctuations, and improper grounding. Below are key best practices for designing and installing a CNC router’s electrical system.
Proper Electrical Design and Planning
Before installing a CNC router, you first need to assess the power requirements and electrical infrastructure of your workspace.
- Voltage and Power Compatibility: Ensure that the CNC router’s voltage and phase requirements (single-phase or three-phase) match the available power supply.
- Dedicated Electrical Circuit: CNC routers should have a dedicated circuit to prevent power fluctuations caused by other machines.
- Load Capacity Assessment: Verify that the electrical panel and wiring can handle the CNC router’s maximum power consumption without overloading.
Certified Wiring and Cable Management
Using high-quality, certified wiring and proper cable management techniques can prevent electrical hazards such as short circuits and overheating.
- Use Industrial-Grade Wiring: Employ wires and cables rated for high-current loads, preferably with fire-resistant insulation.
- Secure and Organize Cables: Route cables away from high-heat or high-movement areas to prevent wear and tear. Use cable trays and conduits to keep wiring organized and protected.
- Avoid Overlapping Power and Signal Cables: Keep power cables separate from signal or communication cables to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Adequate Grounding and Bonding
Proper grounding and bonding are beneficial for reducing the risk of electrical shock, equipment damage, and static buildup.
- Connect to a Reliable Grounding System: Ensure the CNC router is connected to a properly grounded electrical system that meets safety standards.
- Use Grounding Rods if Necessary: In areas with unstable power conditions, consider installing grounding rods to stabilize voltage levels.
- Check Ground Continuity: Regularly test the grounding connection to confirm its effectiveness.
Circuit Protection and Safety Devices
Installing the right protective components helps safeguard the machine and operators from electrical faults.
- Circuit Breakers and Fuses: Use appropriately rated circuit breakers and fuses to protect against overloads and short circuits.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs): Install RCDs to detect leakage currents and quickly shut down power to prevent electrical shock.
- Surge Protectors: Use surge protectors to shield the CNC router’s electronics from voltage spikes caused by lightning strikes or grid fluctuations.
Compliance with Safety Standards and Regulations
Ensuring that the CNC router and its electrical system comply with relevant safety standards is beneficial for operational safety and regulatory compliance.
- Follow International Standards: Adhere to safety regulations such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), NEC (National Electrical Code, US), OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration, US), and CE Certification (European Safety Standards).
- Manufacturer’s Electrical Guidelines: Always follow the electrical installation instructions provided by the CNC router manufacturer.
- Third-Party Inspection: Consider having an electrician inspect the installation to verify compliance with safety standards.
Proper Electrical Panel Setup
The CNC router’s control panel should be designed for accessibility, safety, and ease of maintenance.
- Enclosed Electrical Panels: Use sealed electrical enclosures to protect against dust, moisture, and accidental contact with live wires.
- Labeling and Color Coding: Clearly label wires, terminals, and switches for easy troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Emergency Stop System: Ensure that emergency stop buttons are easily accessible and function properly to disconnect power instantly during emergencies.
Safe Power Connection and Distribution
A well-planned power connection system helps ensure stable operation and minimizes the risk of power fluctuations.
- Stable Power Source: Use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or voltage regulator to provide consistent power and prevent data loss during power outages.
- Avoid Extension Cords and Adapters: Plug the CNC router directly into a properly rated power outlet instead of using extension cords, which can overheat and pose fire hazards.
- Three-Phase Power Balance: For three-phase CNC routers, ensure the power distribution is balanced across all phases to prevent uneven loads and overheating.
Following these design and installation best practices helps prevent electrical failures, enhances CNC router performance, and ensures a safe working environment. Proper planning, high-quality wiring, grounding, circuit protection, and compliance with safety standards form the foundation of electrical safety for CNC routers. The next section will focus on regular inspection and maintenance to ensure long-term safety and efficiency.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Maintaining the electrical safety of your CNC router goes beyond the initial installation and should be regularly inspected and maintained to prevent failures, reduce downtime, and ensure a safe working environment. Electrical components can degrade over time due to dust, vibrations, heat, and continuous operation. A well-structured maintenance plan helps detect issues early and prevent hazardous failures.
Routine Electrical Inspections
Regularly inspecting electrical systems ensures that potential hazards are identified before they become serious problems.
- Visual Inspection of Wires and Cables: Check for frayed, cracked, or exposed wires that could lead to short circuits.
- Inspect Electrical Connections: Tighten loose terminal screws and connectors to prevent overheating or voltage drops.
- Examine Power Supply and Voltage Stability: Use a multimeter to verify that voltage levels are within the machine’s recommended range.
- Test Grounding and Bonding: Measure resistance in the grounding system to ensure a safe electrical discharge path.
- Check Control Panels and Electrical Enclosures: Inspect the CNC router’s control panel for dust accumulation, moisture, or overheating.
Preventive Maintenance for Electrical Components
Scheduled preventive maintenance keeps electrical components in optimal condition and reduces unexpected failures.
- Replace Worn-Out or Damaged Wiring: Any electrical cables showing wear, cuts, or overheating marks should be replaced immediately.
- Test Circuit Breakers and Safety Devices: Trip circuit breakers manually to ensure they function correctly.
- Clean Electrical Contacts and Terminals: Use electrical contact cleaner to keep connections clean and conductive.
- Monitor Fan and Cooling System Performance: Ensure cooling fans are clean, free of dust, and functioning properly.
- Inspect Power Plugs and Sockets: Ensure secure and stable connections at all times.
Testing Safety Systems and Emergency Features
Electrical safety systems in CNC routers must be tested periodically to ensure they function in emergencies.
- Test the Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Button: Press the emergency stop button and verify that the machine powers down instantly.
- Verify Surge Protection Devices: If using surge protectors or voltage regulators, check if they are still functioning correctly.
- Check Alarm Systems and Warning Indicators: Ensure that warning lights, alarms, and system alerts work as expected.
- Verify Software and Firmware Updates: Ensure the firmware and software that controls the electrical safety functions are updated to the latest versions.
Scheduled Maintenance and Record-Keeping
To maintain consistency in safety practices, a structured maintenance schedule should be followed.
- Create a Preventive Maintenance Schedule: Assign specific personnel to document weekly, monthly, and yearly electrical safety checks.
- Keep Maintenance Records: Document any recurring issues to help troubleshoot long-term electrical problems.
By conducting routine checks, performing preventive maintenance, and testing safety systems, manufacturers and operators can prevent costly failures, improve machine longevity, and protect workplace safety. The next section will focus on safety devices and protective equipment that further enhance the CNC router’s electrical safety.
Safety Devices and Protective Equipment
Ensuring the electrical safety of CNC routers involves not only proper design and maintenance but also the implementation of safety devices and protective equipment. These components help prevent electrical hazards, protect operators, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Below are essential safety devices and protective measures that should be incorporated into CNC router operations.
Circuit Protection Devices
Circuit protection prevents electrical overloads, short circuits, and fires.
- Circuit Breakers: Automatically disconnect power when excessive current is detected to prevent overheating and damage to machine components.
- Fuses: Protect against short circuits by breaking the circuit when the current exceeds safe limits.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs) / Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): Detect leakage currents and shut off power to prevent electric shocks.
- Surge Protectors: Absorb sudden voltage spikes from lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations to prevent damage to sensitive electronic components.
Emergency Safety Features
Emergency safety devices protect operators and minimize the risk of accidents.
- Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Button: Allows immediate shutdown of the CNC router during emergencies.
- Overload Protection Relay: Detects excessive power loads and shuts down the machine before damage occurs.
- Thermal Protection for Motors: Monitors motor temperature and automatically shuts down if overheating occurs.
- Fire Suppression Systems: If CNC routers are used in environments with high fire risks, automatic fire suppression systems should be installed in electrical panels.
Protective Electrical Enclosures
Electrical components should be shielded to prevent dust, moisture, and accidental contact.
- Sealed Electrical Cabinets: Protect sensitive electronic components from dust and moisture.
- Cooling and Ventilation Systems: Prevent overheating inside electrical enclosures.
- Lockable Disconnect Switches: Allow technicians to safely power down the machine before performing maintenance.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Electrical Safety
Operators and technicians working on CNC routers should use appropriate PPE to protect against electrical hazards.
- Insulated Gloves: Protect hands from electric shock when working on live electrical panels.
- Safety Shoes with Electrical Insulation: Prevent grounding through the body when operating near high-voltage systems.
- Face Shields and Safety Glasses: Protect against arc flashes and sparks when troubleshooting electrical components.
- Antistatic Wrist Straps: Prevent static discharge when handling sensitive electronics such as CNC control boards.
- Hearing Protection (Optional for High-Frequency Noise): CNC routers with high-speed motors generate electromagnetic noise, which may require hearing protection in long-term exposure environments.
Smart Monitoring and Safety Automation
Advanced monitoring systems improve electrical safety by providing real-time alerts and automation.
- Power Monitoring Systems: Track voltage, current, and power consumption to detect abnormalities before failures occur.
- Automatic Shutdown Systems: Modern CNC routers can include smart sensors that shut down the machine when unsafe conditions (overheating, power fluctuations, or grounding failures) are detected.
- Remote Monitoring via IoT Integration: In industrial setups, IoT-connected safety systems allow real-time tracking of electrical parameters and provide alerts for faults or failures.
Circuit protection, emergency stop systems, electrical enclosures, PPE, and advanced monitoring tools work together to reduce hazards and protect both operators and equipment. The next section will discuss safe operating procedures to minimize risks during CNC router use.
Safe Operating Procedures
Even with proper design, installation, and protective measures, safe operating procedures are essential to minimize the risk of electrical hazards when using CNC routers. Below are key safety procedures operators should follow.
Startup and Shutdown Procedures
A proper startup and shutdown procedure prevents electrical faults, equipment damage, and operational hazards.
- Check Before Starting: Perform a pre-check of all electrical connections, cables, and control panels before powering on the machine and ensure the emergency stop (E-Stop) is functional.
- Power On in the Correct Order: Follow the manufacturer’s sequence for turning on the main power, control systems, and motors.
- Monitor Initial Operation: Observe the startup process to detect unusual noises, sparks, or warning signals.
- Safe Shutdown Procedure: Turn off the spindle and motion system first, and follow the shutdown sequence recommended by the manufacturer.
Avoiding Electrical Work While the Machine Is Running
Performing electrical work on a powered CNC router poses serious risks, including electric shock and short circuits. Here are the key safety measures:
- Never attempt repairs or modifications to electrical wiring, circuit boards, or control panels while the CNC router is powered on.
- Turn off and unplug the machine before accessing internal electrical components.
- Use a lockout/tagout (LOTO) system when performing electrical maintenance to prevent accidental startup.
- Only trained and qualified personnel should handle electrical troubleshooting and repairs.
Keeping Liquids and Metal Shavings Away from Electrical Components
CNC routers generate metal shavings, dust, and coolant spray, which can cause short circuits, corrosion, and component failure if they enter electrical systems. Here are the preventive actions:
- Keep electrical panels, wiring, and control boards enclosed to prevent contamination.
- Use sealed enclosures and protective covers to shield electrical connections from dust and liquids.
- Position the coolant systems carefully to prevent liquid from dripping onto wiring, motors, or circuit boards.
- Regularly clean the work area to remove stray metal shavings and ensure they don’t accumulate near electrical components.
Safe Handling of Plug Connections and Power Switches
Improper handling of power cords, switches, and electrical connectors can cause overheating, arc flashes, and equipment failures. Here are the best practices:
- Always power down the CNC router before plugging or unplugging cables.
- Do not force or pull plugs at an angle, ensure proper alignment to avoid damaging electrical contacts.
- Use only properly rated power outlets and industrial-grade connectors for CNC routers.
- Avoid using extension cords and power strips as they may not handle the high electrical load required by CNC routers.
- Check for loose connections regularly and ensure power cables are routed properly to prevent wear or accidental disconnection.
By following safe operating procedures in these four areas, operators can significantly reduce electrical hazards. Adhering to these safety measures helps maintain machine performance, workplace safety, and compliance with industry regulations. The next section will cover “Staff Training and Safety Awareness” to ensure all CNC operators are knowledgeable about electrical safety.
Staff Training and Safety Awareness
Ensuring the electrical safety of CNC routers requires more than just protective equipment and proper installation—it depends on well-trained employees who understand potential risks and follow safety procedures. A structured training program combined with ongoing safety awareness initiatives can significantly reduce electrical hazards in the workplace. Below are key aspects of an effective employee training and safety awareness program.
Electrical Safety Basics
All CNC router operators should receive foundational training on electrical safety to prevent accidents and ensure proper machine handling.
- Understanding Electrical Hazards: Operators must learn to identify common electrical risks and early warning signs. This helps prevent serious incidents before they escalate.
- Safe Handling of Electrical Components: Operators should be trained to avoid direct contact with live electrical parts and never attempt to repair wiring or circuit boards while the machine is powered on.
- Proper Use of Power Sources and Switches: Training should emphasize the importance of turning the CNC router on and off correctly, avoiding the use of extension cords or overloading circuits.
Emergency Response Training
Operators and maintenance personnel must know how to respond to electrical emergencies to minimize injuries and equipment damage.
- Handling Electrical Shock Incidents: The first step is to cut off the power supply using the emergency stop or main switch. They should never touch the affected person directly if they are still in contact with a live electrical source, use a non-conductive object to separate them from the power source. Calling emergency medical services if necessary should follow.
- Responding to Electrical Fires: Operators must know never to use water to extinguish an electrical fire, they should use a Class C fire extinguisher designed for electrical fires. If the fire is unmanageable, immediate evacuation and calling emergency responders should be the next step.
- Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Procedures: Operators must be trained on the location and proper use of emergency stop (E-Stop) buttons. They should practice pressing the E-Stop in simulated emergencies to ensure quick response times.
Displaying Safety Signs and Labels
A well-marked workplace improves safety awareness and prevents accidental exposure to electrical hazards.
- High-Voltage Warnings: Clearly marked high-voltage warning signs should be placed near CNC router control panels, power supplies, and electrical cabinets.
- Circuit and Component Labeling: Each electrical circuit, fuse, and switch should be labeled to ensure easy identification during troubleshooting or maintenance.
- Fire Safety and Extinguisher Location: Signs indicating the location of fire extinguishers and instructions on how to use a Class C fire extinguisher for electrical fires should be visible.
- Posting Emergency Contact Information: Display contact details for on-site electricians and emergency response teams. Ensure employees know who to call in case of electrical malfunctions or safety concerns.
Regular Refresher Training and Safety Audits
Even experienced operators need ongoing training and safety audits to stay updated on best practices.
- Scheduled Refresher Training Sessions: These sessions should be conducted annually or semi-annually to reinforce knowledge about safe machine operation, grounding practices, and the proper use of safety devices like emergency stop buttons and circuit breakers.
- Routine Electrical Safety Audits: Regular safety audits should be performed to inspect wiring, electrical panels, grounding systems, and machine enclosures for any signs of wear, overheating, or loose connections. These audits help identify and correct potential hazards before they cause failures or accidents.
- Encouraging Employee Feedback: Operators and maintenance staff should be encouraged to report electrical issues or unsafe practices observed during daily operations. Regular safety meetings allow employees to discuss concerns and suggest improvements.
Through the above mentioned safety training content, businesses can drastically reduce the risk of electrical accidents in CNC router operations. A well-informed workforce ensures a safer, more efficient, and regulatory-compliant workplace.
Summarize
Ensuring the electrical safety of CNC routers requires a combination of proper design, regular maintenance, and strict adherence to safety protocols. By identifying common electrical hazards, implementing protective measures, and following safe operating procedures, operators can minimize risks and maintain a safe and efficient workspace. Prioritizing electrical safety not only protects operators and equipment but also enhances productivity and ensures compliance with industry regulations. Electrical safety is an ongoing responsibility that requires vigilance, proactive maintenance, and a strong workplace safety culture.
AccTek CNC routers are designed with advanced electrical safety features, ensuring the safe and stable operation of the machine. Beyond machine quality, AccTek CNC provides expert guidance on operator training, helping businesses maximize machine efficiency. For businesses looking for safe, reliable, and high-performance CNC routers, AccTek CNC is a trusted choice.
